SMART CITY
TMP

AccelNet: Collaborative Research: An International Network of Networks for Well-being in the Built Environment (IN2WIBE)
Over 50% of the world’s population currently lives in cities, and this number is expected to rise to 70% by 2050. This means the total area covered by the cities, hence the built environment, will triple in the next three decades. The built environment has significant impacts on human health and well-being. While existing multidisciplinary networks bring together researchers from human behavioral science, social and economic sciences, data informatics and artificial intelligence, building technology and science, occupational health, a “network-of-network” to facilitate the convergence research is currently lacking.
Our proposed AccelNet at Full-Scale Implementation level aims to accelerate advancements in human wellness to inform better building design and operations as well as education of the next generation of professionals with a multidisciplinary background. We attempt to answer new questions that arise from connecting separate networks, such as how the built environment affects occupants’ wellness, how new technologies in data and measurement may fundamentally change the relationship between humans and the built environment, and above all, how differences in culture and climate affect health and well-being within the human-building-environment paradigm. This will be achieved through leveraging resources from the existing networks in the U.S., UK, Ireland, Sweden, Switzerland, Denmark, Italy, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, Singapore, Middle East, etc., and cultivating and fostering connections through the development and implementation of community standards including the data collected from people and buildings in different cities. Such big data will include multiple sources of human well-being and built environment data. The overarching research themes are aligned with two of the NSF 10 big ideas: Future of Work at the Human-Technology Frontier and Harnessing the Data Revolution.
The activities of the AcceltNet include: 1) collectively develop protocols of a data infrastructure to allow sharing the data about humans and built environments across the world; 2) create collaborative and networking technologies (e.g., annual retreat, workshops, etc.) to facilitate the convergence of mission and goals among the participating networks; and 3) prepare the next generation of professionals with a diverse background through international collaborative educational activities (e.g., exchange students, co-advise students, etc.).
BuildAPP
The purpose of this project was to create and promote a consumer-driven advanced intelligent building application aiming to better align the existing building features with the managers, owners and tenants priorities. We intend to provide this application for free to your tenants and further develop a project that has never been associated with a consumer focus.
The project consists of four distinct modules, as mentioned in our presentation:
- Module 1: Identity Management
- Module 2: Information
- Module 3: Consumer Services
- Module 4: Energy Control
The technology that will be used is the Indoor Atlas Application instead of the Beacon Technology Solution for the following reasons:
- Beacons work with Bluetooth technology. Therefore, in order to work properly, users will be required to keep their phone’s Bluetooth on all day.
- During similar app developments, it was observed that users that downloaded and kept the app, preferred to switch off their Bluetooth to prevent battery draining. As a result, no data were transmitted and the app remained inactive.
- Even if users keep the app and the Bluetooth on, there is no way to reassure the accurate transmission of data, as beacons can only be accessed through the phone – there is no other indicator of the beacon activity.
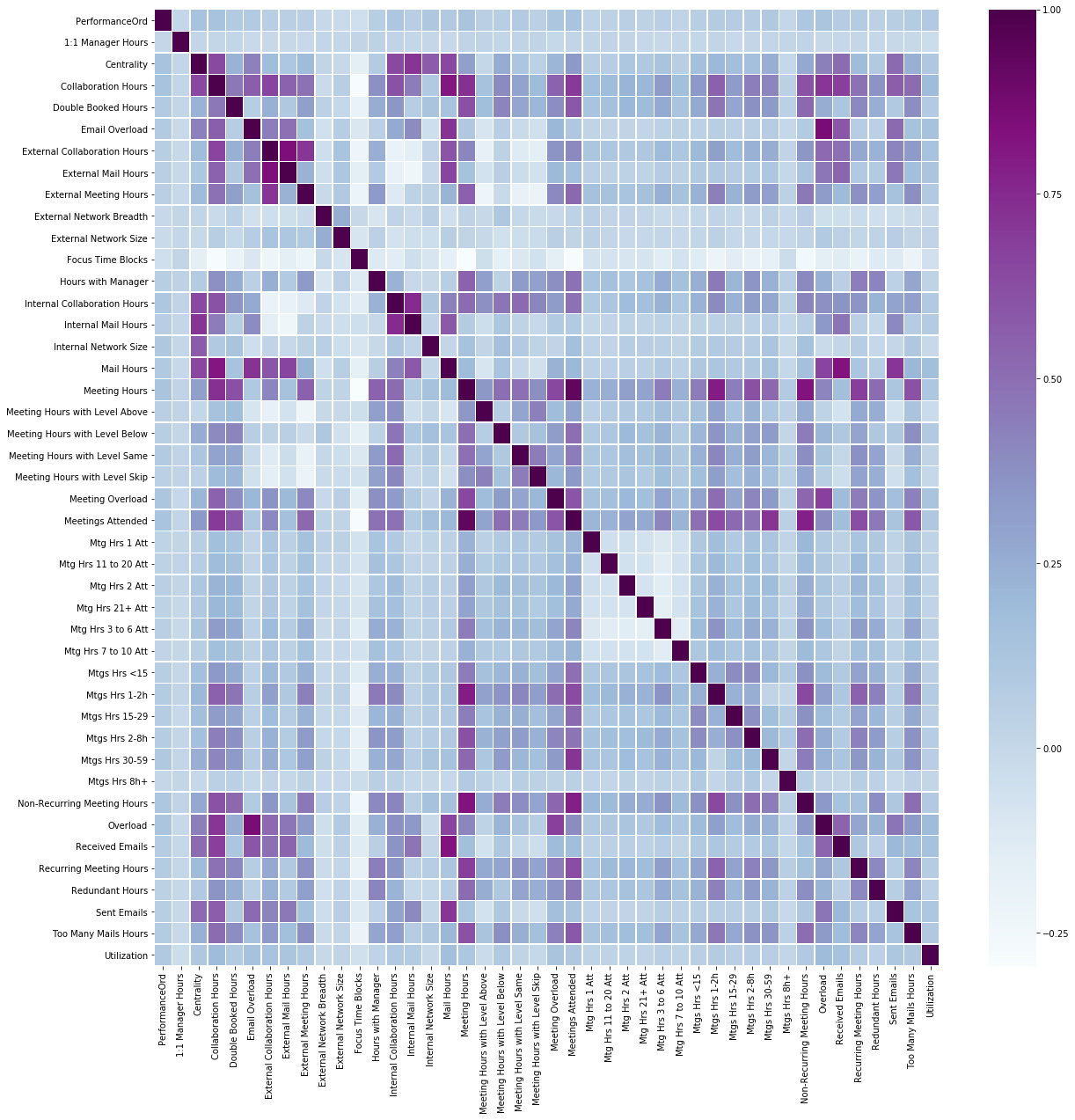
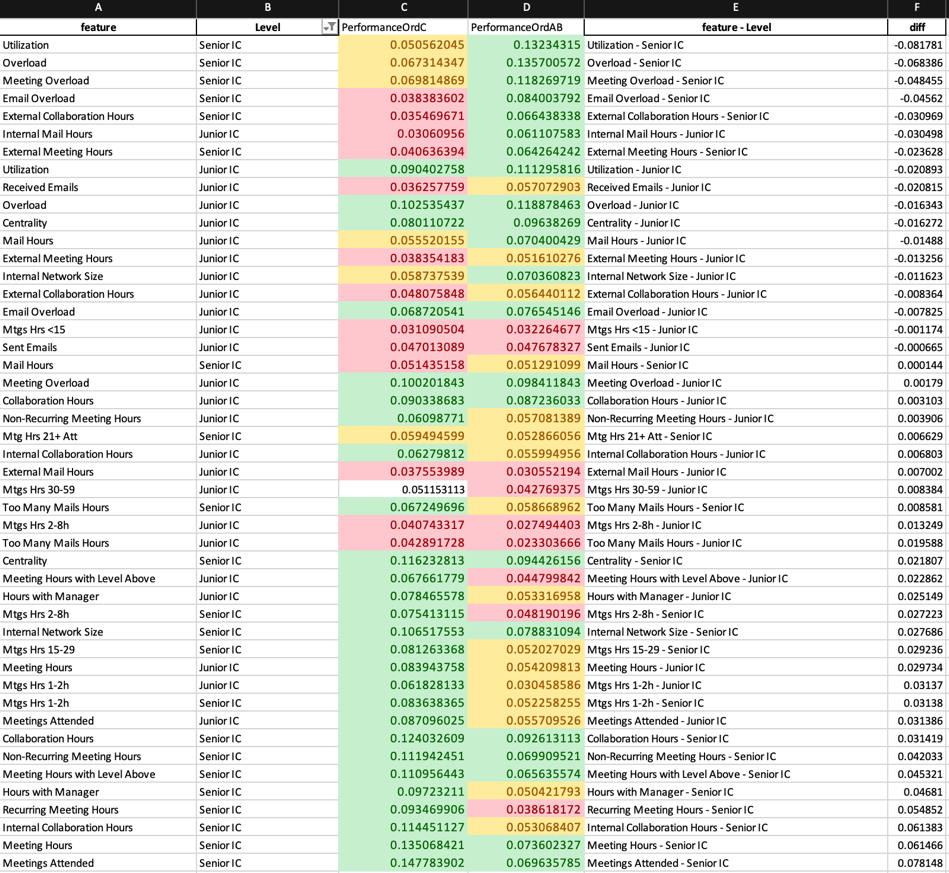
Hyperconnected spaces and productivity
How gathering and working with data was able to allow us to identify how spaces affect peoples’ productivity. We worked with data to understand what affects employees’ engagement with senior management, how workload is a parameter to drive results and how the distribution of people in a smart space can lead to a better much more coordinated effort and management.
Our goal is to identify the variables that can affect the design of a space and make the area capable of addressing the needs and requirements of users sitting in various levels of hierarchy.
Autonomous buildings
The work we are doing is on defining what an autonomous building is and how democratic can be in a post-pandemic era. What technologies shall be used, how data can be stored and how we can use AI to protect privacy. The goal is to form the description of a building capable to be fully autonomous when it comes to meet the needs of its users